|
THE
SYSTEMS OF SUPERSENSIBLE FORCES
LECTURE 5
24th March, 1911.
IT
will be my task to-day, before we continue our
studies, to present certain concepts which we shall need to use in
the further development of our discussions. In this connection it
will be especially important for us to come to an understanding as
regards the meaning of that which we call in a spiritual-scientific,
anthroposophical sense, a “physical organ,” or rather the
“physical expression of an organ.” For you have already
seen that we have a right to say with regard to the spleen, for
example, that, as something material, the physical spleen may even be
removed or become useless without thereby causing the activity of
what we call “the spleen” in the anthroposophical sense
to be eliminated. We must say, then, that when we have actually
removed a physical organ such as this, there still remains in the
organism the inner vital activity which should be carried on by the
organ. From this we already see, and I beg you most earnestly to
adopt this concept for all that follows, that we can think away, as
it were, everything physically visible and perceptible in an organ
such as this (it is not possible in the case of every organ) and yet
there still remains the functioning, the activity of the organ, with
the result that we must consider what then remains as belonging to
what is super-sensible in the human organism. But, on the other hand,
when we speak on the basis of our spiritual science about such organs
as the spleen, the liver, the gall-bladder, the kidneys, the lungs,
and the like, we are by no means referring when using these names, to
what we can see physically, but rather to force-systems that are in
reality of a super-sensible nature. For this reason, precisely in the
case of such an organ as the spleen we must think, to begin with,
when we speak about it from the spiritual-scientific standpoint, of a
force-system not physically visible to external sight.
Let us then, in the
first sketch that I shall draw here, think of a force-system not
physically visible. This would represent a force-system visible only
to super-sensible vision; and a system such as that in the region of
the spleen, for example, would be visible only as a super-sensible
force-system. Now if we bear in mind that, in the actual human
organism which we have directly before us, this super-sensible
force-system is filled out with physical matter, we must ask
ourselves how we shall have to think of the relationship between it
and that which is sense-perceptible matter.
I am sure it will not
be difficult for you to believe that forces not visible to the senses
can traverse space. One need only recall, for example, the following:
Anyone who had never heard anything about the reality of air in a
bottle would be rather surprised if we were to place an empty bottle
on a table and tightly insert a funnel in it, when, on pouring water
quickly into the funnel the water in the funnel is held there and
cannot flow down into the bottle because the latter contains air. He
would then become aware of the fact that there is, indeed, in the
bottle something invisible to him which holds back the water. If we
imagine this concept carried somewhat further, it will not be
difficult to think that space around us may likewise be completely
filled with force-systems which are obviously of a super-sensible
nature, moreover, of such a super-sensible nature that not only can we
not cut through them with a knife, but that they cannot be affected
when any physical matter such as the kidneys, embedded within these
force-systems, becomes diseased. We must realise, therefore, that the
relation between a super-sensible force-system of this sort and what
we see as a physical-sensible organ is such that physical matter,
belonging to the physical world fits itself in and, attracted by the
force-centres, deposits itself within the lines of force. Through the
depositing of the physical matter in the super-sensible force-system
does the organ become a physical thing. We may say, therefore, that
the reason why, for instance, a physical-sensible organ is visible at
the place where the spleen is located is that, at this point, space is
filled in a certain definite manner by force-systems which attract the
material substance in such a way that this deposits itself in the form
in which we see it in the external organ of the spleen when we study
it anatomically.
| | 
Diagram 17
Click image for large view | |
So you may think of
all the different organs in the human organism as being first planned
as super-sensible organs, and then, under the influence of the most
varied sorts of super-sensible force-systems, as being filled with
physical matter. Hence, in these force-systems which at different
points of the organism deposit physical matter within themselves, we
must recognise a super-sensible organism which is differentiated
within itself and which incorporates physical matter within itself in
the most diverse ways. We have thus obtained, not only this one
concept of the relation of the super-sensible force-systems to the
physical matter deposited in the organs, but also the other concept
of the process of nourishing the organism as a whole. For this
process of nourishing the entire organism consists in nothing else,
after all, than in so preparing the nutritive substances taken in
that it is possible to convey them to the different organs, and then
in the incorporating of these substances by these organs. We shall
see later how this general concept regarding the process of
nutrition, which appears to be a power of attraction in the different
organ-systems for the nutritive substances, is related to the coming
into existence of a single human being, the embryonic development of
the single human being which takes place before birth. The most
comprehensive concept of nutrition, accordingly, is this: that by
means of a super-sensible organism, the different nutritive substances
are absorbed in the greatest variety of ways.
Now we must bear
clearly in mind that man's ether-body, the super-sensible member
of the human organisation nearest to the physical body, is the
coarsest, so to speak; but that it underlies the entire organisation
as its super-sensible prototype, is differentiated within itself, and
contains the most manifold sorts of force-systems, in order that it
may incorporate in the greatest variety of ways the substances taken
in through the process of nutrition. But, in addition to this etheric
organism, which we may look upon as the nearest prototype of the
human organisation, we have still a higher member in the so-called
astral body. (Just how these things are inter-related we shall see in
the course of these lectures.) The astral body can become a member of
the organism only when the physical and the etheric organisms have
each been prepared according to its disposition. The astral body is
that which presupposes both the other organisms. We have, moreover,
the ego; so that the human being is composed of a union of these
four members.
Now, we may picture
to ourselves that even in the ether-body itself there are certain
force-systems that attract to themselves particles of food taken in,
and then shape these in quite definite ways in the physical organism.
But we can also picture to ourselves that such a force-system is
determined not only by the ether-body but also by the astral body,
and that the latter sends its forces into the ether-body. If
accordingly we first think away the physical organ and conceive the
physical matter as cut out we have, first, the etheric force-system
and next the astral force-system, which in turn permeates the etheric
force-system in a perfectly definite manner. Indeed we may also
conceive radiations passing down into these from the ego.
Now there may be
organs which are so incorporated in the whole organism that their
essential characteristic, for example, lies in the fact that the
etheric currents in them are, as yet, very indefinite. We find,
therefore, if we investigate the space in which such an organ is
located, that the etheric portion of the human organism in this
spatial formation is very slightly differentiated in itself, contains
very little in the way of force-systems; but that, to make up for
this, these weak forces of the ether-body are influenced by strong
astral forces. When, therefore, physical matter is incorporated into
such an organ as this, the ether-body exercises only a slight force
of attraction and the chief forces of attraction must be exercised by
the astral body upon the organ in question. It is as if the relevant
substances are brought, as it were, by the astral body into this
organ. From this we see that the values of the human organs here in
question vary considerably. There are certain organs which we have to
recognise as being determined principally through the force-systems
of the ether-body; and others which are determined, rather, through
the currents or forces coming from the astral body; whereas others
again are to a greater degree determined through the currents of the
ego.
Now, as a result of
all that has thus far been presented in these lectures, one may say
that especially that organic system conveying our blood is
essentially dependent upon the radiations going forth from our ego;
and that the human blood, therefore, is connected essentially with
the currents and radiations of the human ego. The other
organ-systems, with what they contain, are determined in the greatest
variety of ways by the super-sensible members of man's nature.
But the reverse
situation may occur when we consider the physical body per
se, which, indeed, disregarding for the moment its higher
members, exhibits likewise a force-system. For it represents, to
begin with, what we may conceive as the combination of all the
substances taken in from the outer world which at the same time have
brought into it their own inner forces, even though in a transformed
condition. Thus the physical body is also a force-system; also a
force-system; so that we may also imagine cases in which this
physical organism with its force-system works back upon the etheric,
or even upon the astral, force-system, indeed even as far back as the
ego-system. Not only may we conceive that the etheric force-system is
seized upon by the astral- or the ego-system, but it is equally
possible that there are organic systems which are specially
requisitioned by the physical force-systems, in which cases it is the
physical force-systems that prevail. Organ-systems of this sort, in
which the physical body preponderates over the others, and which are
therefore only to a lesser degree influenced by the higher members of
the human organisation — while on the other hand more strongly
influenced by the laws of the physical body — these are more
especially the organ-systems which serve in a very comprehensive
sense as organs of secretion and excretion,
[ 1 ]
as glandular organs or secretory and excretory
organs in general. All organs of secretion, therefore, organs which
secrete substances directly in the human organism, are induced to do
so — a process that has its essential significance purely in
the physical world — chiefly through the forces of the physical
organism. Wherever in the human body there are organs such as these,
existing for the special purpose of being used by the physical
organism to secrete substances, such organs, when they become ill or
are removed — which means when they become useless in some
quite definite way — cause the ruin of the organism so that it
cannot any longer continue its normal development.
In the case of an
organ like the spleen, with regard to which the statement was
ventured in yesterday's lecture that, when it becomes ill or in
any way useless, its own function is affected less than would be true
in the case of other organs, we see that it is very specially
influenced by the super-sensible portions of man's nature, by
the ether-body and more especially by the astral body. And we see
that in the case of some other organs the physical forces
predominate. The thyroid gland, which in certain disease conditions
becomes enlarged into the so-called goitre, may have a very injurious
influence upon the whole organism, because the activities which it
especially has to manifest are such that what it brings about in the
physical world as a physical process is absolutely essential to the
general economy of the human organism.
Now there may be
organs that are to a very high degree dependent upon the other, the
super-sensible force-systems of the human organism, but which are none
the less closely bound to the physical organism and are induced
through its forces to secrete physical matter. Such organs, for
example, are the liver and the kidneys. These are organs which, like
the spleen, are dependent upon the super-sensible members of the human
organisation, the ether-body and the astral body, but which are
seized upon by the forces of the physical organism, and are drawn
downward in their activities even into the forces of the physical
organism. It is, therefore, of far greater importance for them to be
in a healthy condition as physical organs in the human organism than
for other organs, those, for example, in which conditions are such
that the physical demands are far outweighed by what is derived from
the other members, so that we have in the spleen an organ of which we
can say that it is a very spiritual organ, that is, the physical part
of this organ is its least significant part. In occult literature
which has come forth from circles where something was really known
about these matters, the spleen has always been looked upon as a
particularly spiritual organ and is described as such.
Thus we have now
arrived at what we may call the concept of the “complete
organ.” An organ, as such, may be looked upon as a
super-sensible force-system; although physical-sensible substances are
stored up, as it were, in the organs through the entire process of
nutrition. Another concept we must acquire raises this question: What
is the significance in general of taking in something, whether it be
a physical substance or what is received through the influence of our
soul-activity; for example, through perception? And what is the
significance of the excreting
[ 2 ]
of a physical substance?
Let us begin with the
process of excretion in its most inclusive sense. We know, in the
first place, that from the food taken, a large portion of the
material substance is excreted. We know, further, that carbonic acid
is excreted from the human organism through the lungs; that, after
the blood has been sent out of the heart and through the lungs in
order to be renewed, the carbonic acid is thrown off. We have, then,
another excretory process through the kidneys, but also one through
the skin. In this last process which goes on primarily in the forming
of perspiration, but also in everything occurring by way of the skin
which must be classed as an excretory process, we have those
excretory processes in the human being which take place at the
outermost circumference of the body, its outermost periphery. Let us
now ask ourselves the question: What is the full significance of the
excretory process in the human being?
Only in the following
way can we be clear as to the significance of a process of excretion.
You will see that, without such concepts as we are developing to-day,
it will be impossible for us to get any further with our study of the
human organism. I should like, in order to be able gradually to carry
forward our thinking to the essential nature of a process of
excretion, first to submit for your consideration another concept
which has, to be sure, only a remote similarity to the excretory
processes, but which can nevertheless guide us to them, namely, the
concept of the becoming aware of our Self.
Think for a moment,
how is it really possible after all to affirm that there is such a
thing as the becoming aware of one's Self? If you move
incautiously in a room and stumble against some external object you
say that you have run into something. This impact is actually a
becoming aware of your own Self in such a way, that the collision has
in reality become for you an inner occurrence. For what is the
collision with a foreign object so far as it affects you? It is the
cause of a hurt, a pain. The process of feeling pain takes place
entirely within yourself. Thus an inner process is called forth by
the fact that you come into contact with a foreign object, and that
this constitutes a hindrance in your way. It is the becoming aware of
this hindrance that calls forth the inner process which, in the
moment of collision, makes itself known as pain. In fact, you can
easily conceive that you do not need to know anything else whatever
in order to experience this becoming aware of your Self except the
effect, the pain, caused by coming into contact with an external
object. Imagine that you stumble against an object in the dark
without knowing at all what it is, and that you hit it so hard that
you do not even stop to think what it might be, but notice only the
effect in the pain.
In this case you have
felt the blow in its effect in such a way that you live through an
inner process within yourself. You are not inwardly conscious of
anything but an inner process in such a case, where you think of the
blow as having taken place in the dark and of your having experienced
its effect in pain. Of course, you say to yourself “I have run
into something,” but this is nevertheless a more or less
unconscious conclusion resulting from your inner experience of the
outer object.
From this you can see
that man becomes aware of his inner Being in the sensing of
resistance. This is the concept we must have: becoming aware,
consciousness of inner life, of being filled with real inner
experiences through the sensing of a resistance. This is somewhat the
concept which I have here developed in order to be able to make the
transition to another concept, that of the excretions in the human
organism. Let us suppose that the human organism takes into itself in
some way or other, into one of its organ-systems, a certain kind of
physical substance, and that this organ-system is so regulated that
through its own activity it eliminates something from the substance
taken in, separates it from the substance as a whole, so that through
the activity of this organ the original complete substance falls
apart into a finer, filtered portion and a coarser portion, which is
excreted. Thus there begins a differentiating of the substance taken
in, into a substance that is further useful, which can be received by
other organs, and another that is first separated and then excreted.
The unusable portions of the physical substance are thrust away in
contrast with the usable portions, an expression here justified, and
we have such a collision as I described roughly in the case of
one's running against some outer object. The stream of physical
matter as a whole, when it comes into an organ, runs against a
resistance as it were; it cannot remain as it is, it must change
itself. It is told by the organ, as we might say: “You cannot
remain as you are; you must transform yourself.” Let us suppose
that such a substance goes into the liver. There it is told,
“You must change yourself.” A resistance is set up
against it. For further use it must become a different substance, and
it must cast off certain portions. Thus it happens in our organism
that the substance perceives that resistance is present. Such
resistances are to be found within the entire organism in a great
number of different organs. It is only because secretion takes place
at all in our organism, because we have organs of secretion, that it
is possible for our organism to be secluded within itself; to be a
self-experiencing being. For only so can any being become conscious
of its own inner life, through the fact that its own life meets with
resistance. Thus we have in the processes of secretion processes
important for human life — processes, in other words, by means
of which the living organism secludes itself within itself. Man would
not be a Being secluded within himself if such processes of secretion
did not take place.
Let us suppose that
the flow of nourishment or of oxygen that has been absorbed, were to
pass through the human organism as if through a tube. The result, if
no resistance were offered through the organs, would be that the
human organism would not be conscious within itself of its own inner
life but would experience itself; on the contrary, only as belonging
to the great world as a whole. We might, to be sure, imagine also
that the crudest form of this resistance were to appear in the human
organism, that the substance in question might knock itself against a
solid wall, and turn back again into itself. This would not, however,
make any difference to the inner experience of the human organism;
for whether a flow of food or of oxygen were to pass through the
organism, entering at one end and passing out at the other, being
reflected back on itself as through a hose, this would not make any
real difference to an inner experience of the human organism. That
this is so we can at once gather from the fact that, when we bring it
about in our nervous system that a concept turns back into itself, we
thereby lift our nervous system right out of the inner experience of
the human organism. It makes no difference why the human organism is
left unaffected, whether because the streams entering from without
are completely reflected or merely pass through. What makes it
possible to realise the inner life of the human organism is the
processes of secretion.
Now if we observe
that organ which we must consider the central organ of the human
organism, the organ of the blood, noting how it continually renews
the blood in one direction by taking in oxygen, and if we see in this
organ the instrument of the human ego, we may then say that if the
blood were to go through the human ego unchanged, it could not in
that case be the instrument of the human ego, that which in the very
highest sense enables man to be conscious of his own inner life. Only
through the fact that the blood undergoes changes in its own inner
life, and then goes back as something different, in other words, that
something is excreted from the changed blood, only because of this is
it possible for man, not only to have an ego, but to
experience it inwardly with the help of a physical-sensible
instrument.
We have now
enunciated the concept of the process of excretion. We shall
next have to ask ourselves how it is with that excretion pertaining
to the outermost boundary of the human organism. It will certainly
not be difficult for us to conceive that the human organism as a
whole must operate in such a way that this excretion can take place
just where it does, on the periphery. For this purpose it is
necessary that, confronting all the streams of the human organism,
there should be one organ which is connected with this most extensive
of all the processes of excretion. And this organ which is, as you
will readily surmise, the skin in its most comprehensive sense
together with everything pertaining to it, presents most directly to
the view what we call essential in the human form. When we
picture to ourselves, therefore, that the human organism can be
inwardly conscious of its own life at its outermost periphery only
through the fact that it has placed the organ of the skin where it
confronts all its various streams, we are obliged to see in the
peculiar formation of the skin one of the expressions of the
innermost force of the human organism.
How shall we think of
the skin-organ with everything pertaining to it? We shall see later
in detail what it is that pertains to it, but to-day we shall
characterise these relationships as a whole.
Here we must be clear
about one thing. In what belongs to our conscious inner experience,
about which we can still have a kind of knowledge through some sort
of self-observation, there is not to be included that structure which
comes to expression in the form of our skin. Even though we are still
actively sharing in the fashioning of the outer surface of our body,
this active sharing is such that we may say all directly voluntary action
is completely excluded. It is true that as regards the mobility
of the surface of our body, in our facial expression, gestures, etc.,
we have an influence which still extends to what we may call our conscious
activity; but in the actual formation we have no longer any influence.
It must, of course, be admitted that man does have a certain influence
within narrow limits upon the outer form of his body through his inner
life between birth and death. With regard to this anyone can convince
himself who has known a man at a certain definite time of life, and
who then sees him again after perhaps ten years. Especially is this
true if, during these ten years, this man has gone through profound
inner experiences, and especially those connected with the acquiring
of knowledge, not such knowledge as constitutes the subject-matter of
external science, but rather those which cost blood and are connected
with the destiny of the whole inner life. We then see, indeed, how within
certain narrow limits the physiognomy changes; how to a certain extent,
therefore, man does have within these limits an influence upon the formation
of his body. Yet he has it only to a very slight degree, as anyone will
have to admit; for the most essential share in the forming of man is
not entrusted to his volition with the help of what reaches him through
his consciousness. On the other hand we must admit that the entire human
form is adapted to man's essential being. Anyone who looks into these
things will never for a moment imagine that what we mean by the whole
range of human capacities could develop in a being having any other
form than the human form as it exists in the physical world. Everything
in the way of human capacities is related to this human form. Just suppose
for a moment that the frontal bone were in any other position with relation
to the whole organism than what it is; in that case you would have to
suppose that this different position of the frontal bone, this changing
of form, would presuppose at the same time entirely different capacities
and forces in man. It is possible, indeed, to make a study of this in
mankind as one comes to see clearly that there are different capacities
among human beings having a different outer formation of the head or
other organs. This is the way, then, that we must create for ourselves
a concept of the conformity of the human form to man's being in its
totality, of the complete correspondence between the outer form and
the essential quality of man's entire being. What lies in the forces
that are active in this adaptation has nothing to do with what enters
into man's own activity within the compass of his own consciousness.
Since, however, man's form is connected with his spiritual activity,
and with his soul-life as well, it would not be possible to imagine
otherwise than that the forces which bring about the human form are
those which come from another direction, to meet the forces that man
himself develops within his form. Here within him are the forces of
intelligence, of feeling, of temperament, etc. These the human being
can develop only in the physical world, as conditioned by his particular
form. This form must be given to him. Whatever capacities of ours need
this form must receive it already prepared, if I may express it thus,
from corresponding forces of a similar kind, which, working from the
other direction, first build up the form in order that these capacities
may be used as they ought to be used. It is not difficult to gain this
concept. We need only think of a case like the following. When we have
a machine which is to be used for some intelligent activity, some activity
that has a purpose, we have to do in the first place with the machine
and this purposeful activity. In order, however, that the machine may
come into existence, it is necessary that similar activities be carried
out, which assemble the parts of the machine and give form to the whole.
These activities must be similar to those which are later carried on
by means of the machine itself. We must say, therefore, that when we
observe a machine it is wholly and absolutely explicable on mechanical
principles; but the fact that the machine is adapted to its purpose
requires us to suppose that it came into existence through the activity
of a mind which had thought out that purpose beforehand. This spiritual
activity has withdrawn, to be sure, and does not need to be brought
forward when we wish to explain the machine scientifically; yet it is
there, behind the machine, and first produced it.
So likewise can we say
that, for the developing of our capacities and powers as human beings,
we need above all those systems of forms which lie within the moulding
of our organism. There must be behind this human form, however, forces
that do the forming, which we can as little find in the already fashioned
form as we find the builder of the machine in the machine itself.
Through this idea something
else will become quite clear to you. A materialistic thinker, for instance,
might come forward and say: “But why do we need to assume that
there are intelligent forces and beings behind that which gives form
to our physical world? We can, indeed, explain the physical world through
itself, by means of its own laws: a watch or a machine, for example,
can be explained by means of its own laws.” Here we have arrived
at a point where the worst kind of errors appear, on this side and that,
where from the anthroposophical standpoint also, or among those who
stand for some other spiritual world-conception, such errors occur.
If it should be disputed, for example, by a spiritual-scientific world-conception
that the human organism as it presents itself to us and which we are
now observing according to its form, can be explained purely mechanically,
or mechanistically through its own laws, that would naturally be going
too far and would be quite unjustified. The human organism is, indeed,
absolutely and entirely explainable out of its own laws, just as is
the watch. Yet it does not follow from the fact that the watch can be
explained by means of its own laws that the inventor was not behind
the watch. This objection, accordingly, answers itself through the very
fact that it must be admitted that the human organism must be explained
on the basis of its own laws.
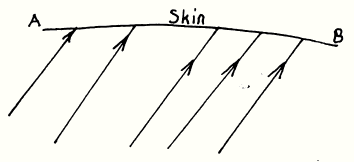
When we think, therefore,
from the point of view of spiritual science, we have first to seek behind
the form of a man as a whole for the form-creative beings — that
is for what underlies this entire human being. If we wish to form a
concept of how the human form comes to be at all, we must think of it
as coming about on the one side through the fact that the form-giving
forces unfold themselves, and that in the building up of this human
form they at first enclose themselves within it. We have presented to
us, accordingly, in the formation of the skin, the most extensive circumference
spatially of that which stands for the self-enclosing of the formative
forces in man. We might draw a sketch and think of of these form-giving
forces in man as flowing outward and enclosing themselves within the
outer form, which shall here be indicated simply by the line AB. It
will becom clear to us that we shall have further need for this concept
in order to understand what goes on at this outermost circumference
of the human being, anywhere inside the skin. There is something else,
however, about which we must be clear: that not only within the human
skin do we find such enclosing, but also within the human organism itself
we have the same sort of self-enclosing of the activity and fullness
of being which work into it from outside. You need only reflect upon
all that has been said up to this point and you will remember that we
do find just such self-enclosing activity inside the human being, one
in which we take no more part than in the forming of our skin-surface.
We mean here those very activities which come about in the organs of
the liver, the gall-bladder, the spleen, etc. That which streams into
the organism by means of the forces contained in the nutritive substances
is stopped by these organs. Something is pushed against it; a resistance
is set up in opposition to it. In other words here in these organs the
external vital activity of these substances is transformed. Whereas,
therefore, in the case of the form-giving forces within us, it is necessary
to think of these as being active as far as the skin, and whereas outside
the skin we find no more form-giving forces, we must picture to ourselves
that in the case of those forces which enter into us with the stream
of nutrition or air, there is not a complete enclosing of what finds
its way inward as currents from without, but rather there takes place
a transformation. We must not think of these organs as stopping something,
as is the case with the skin, but must rather think that the vital activity
of the substances is so changed by them that the stream of food taken
in by these organs (a) is then conveyed further in a changed
form (b) after it has met with resistance. Thus we have here
to do with a process of change, and this concerns especially those particular
organs which we have characterised as the inner cosmic system in man.
They change the external movements of the substances. These are forces
which, in contrast to the form-forces that build up the whole organism,
we may call forces of movement. Within our inner cosmic system
these forces, which transform the inner vital activity of the nutritive
substances, themselves become movement; so that we can rightly speak
here of forces of movement in these organs.
| | 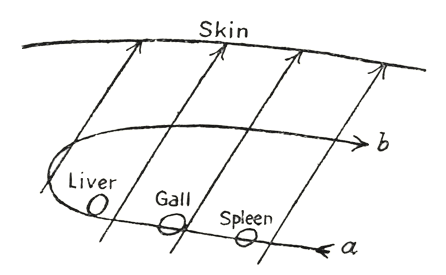
Diagram 18
Click image for large view | |
We are now far enough
advanced in our considerations to be able to say that there are
forces which work from outside into the human organism, forces whose
activity we cannot compass within the horizon of our consciousness.
All that we can refer to as “activities” in this case takes
place below the threshold of our consciousness, for certainly no one in
a normal state of consciousness can observe the activity of his liver,
his gall-bladder, spleen, etc. And now, since our whole nervous
system is a member of our organism, the question arises: what
prevents this nervous system from knowing something about the
formation of the organs in this organism? This certainly does take
place there; the forces that give us our form are at work in our
organism, and similarly those within our inner cosmic system which
change the movement and the vital activity of substances. How does it
come about that we know nothing of all this?
The nervous system of
our brain and spinal cord is intended, in a normal state of
consciousness, to convey external impressions to the blood, that is,
to take the impressions in as physical processes in such a way that
these processes beat against the blood, as it were, and in doing this
inscribe themselves upon the instrument of the ego, the blood, so
that the outer impressions are thereby transferred to it. And just as
truly the branches of the sympathetic nervous system which, with its
ganglions and ramifications, stands guard over the inner cosmic
system, are intended to keep the processes that go on in this inner
cosmic system from approaching as far as the blood, to hold these
processes back, so to speak. You have now heard something more in
regard to what I have previously touched upon, namely, that the
sympathetic nervous system has a function contrary to that of the
nervous system of the brain and spinal cord. Whereas the latter must
make the effort to convey external impressions to the blood in the
best possible way, the sympathetic nervous system, with its opposite
activity, must be continually holding back from the blood, from the
instrument of the ego, the transformed vital activities of the
substances that have been taken in. If we observe the digestive
process, we have there, first, the taking in of external nutritive
substances; then the holding back of the vital activities peculiar
to these nutritive substances, and the transformation of these by
means of the inner cosmic system of man. The vital activities of
these substances, accordingly, are changed into other sorts of vital
activities. In order that we need not, placed as we are in the world,
continually perceive inwardly what goes on in our inner organs, this
entire stream of processes must be held back from the blood by means
of the sympathetic nervous system, whereas that other nervous system
goes to meet what is taken in from outside.
Here, then, you have
the function of the sympathetic nervous system, which becomes a part
of our organism for the purpose of holding our inner processes, not
allowing them to penetrate to the ego-instrument, the blood. I called
your attention yesterday to the fact that the outer life and the
inner life of man, as they are expressed in the ether-body, present a
contrast; and that this contrast between the inner life and the outer
is expressed in tensions which finally come to a climax, as we saw,
in those organs of the brain called the pineal gland and the
pituitary body.
Now, if you put
together yesterday's and to-day's discussions, you will
be able to understand that everything which beats in upon us from
outside, in order to stand in the closest possible contact with the
circulation of the blood, strives to unite with its counterpart, with
what is held back by the sympathetic nervous system. For this reason
we have, in the pineal gland, the place where what has been brought
to the blood by means of the nervous system of the brain and spinal
cord unites with what approaches man from the other direction; and
the pituitary body is there as a last outpost to prevent the approach
of what has to do with the life of the inner man. There are opposite
to each other, at this point in the brain, two important organs.
Everything that we live through in our inner organisation remains
below our consciousness; for it would, indeed, be terribly disturbing
to us if we were to share consciously in our whole process of
nutrition. This is kept back from our consciousness by means of the
sympathetic nervous system. Only when this reciprocal relationship
between the two nervous systems, as this is expressed in the state of
tension between the pineal gland and the pituitary body, is not in
order does something result which we may call a “glimmering
through from the one side to the other,” a being disturbed on
the one side by the other. This takes place when some irregularity in
the activity of our digestive organs expresses itself in our
consciousness in feelings of discomfort. In this case we have a
raying into the consciousness, although very obscure, of the internal
life of the human being, which has first been changed with the help
of the inner cosmic system from the form it had in the life outside.
Or in special emotions, such as anger and the like — which have
a particularly strong influence on man, originating in the
consciousness, we have a breaking through from the other direction
into the organism. We then have one of these cases in which emotions,
unusual inner disturbances of the soul, can influence in a specially
harmful way the digestion, the respiratory system and also,
consequently, the circulation of the blood and everything that lies
below consciousness.
It is thus possible
for these two sides of human nature to act reciprocally upon each
other. And we are obliged to state that, as human beings, we actually
stand in the world as a duality: a duality in the first place which
has, in the nervous system of the brain and the spinal cord,
instruments that bring external impressions to the blood, the
instrument of the ego. From this whole stream of soul-life is held
back, by means of the sympathetic nervous system, everything in the
way of inner realisation of the life of the organs. These two streams
confront each other all along the line, so to speak; but we find
their special expressions in those two organs of which we spoke at
the close of yesterday's lecture. From this point we will
continue our considerations in the next lecture.
Notes:
1.
Absonderungsorgane. The term Absonderung is applied in
these lectures to the process whereby various organs take out a portion
of the nutritive matter and hold this for use (=secretion)
and at the same time reject the rest of the matter
(=excretion), either discharging this portion out of the
body or passing it on to be discharged. The important aspect of
the process, from the point of view of these lectures, is that of
separation, implying resistance, through which alone man can
become conscious of himself. Hence the term excretion is used for
Absonderung except where secretion is obviously required.
2.
See footnote, p. 79.
|